Historical Information: Difference between revisions
imported>Laimab No edit summary |
imported>Laimab No edit summary |
||
| Line 210: | Line 210: | ||
Typically MRS data is collected within a single voxel that needs to be manually prescribed. Manual prescription can lead to systematic bias and low data quality that may be caused by inexperienced users or inter-individual placement variability. To avoid these issues, and improve data collection quality, Matthew Sacchet has developed an automated voxel placement tool. It uses non-linear warping between native subject space and template space to identify precise voxel locations in scanner space. The tool is used in real-time during data acquisition and has been streamlined for efficient usage and low time cost. | Typically MRS data is collected within a single voxel that needs to be manually prescribed. Manual prescription can lead to systematic bias and low data quality that may be caused by inexperienced users or inter-individual placement variability. To avoid these issues, and improve data collection quality, Matthew Sacchet has developed an automated voxel placement tool. It uses non-linear warping between native subject space and template space to identify precise voxel locations in scanner space. The tool is used in real-time during data acquisition and has been streamlined for efficient usage and low time cost. | ||
Review papers of MRS of GABA: | |||
[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0079656511000434 In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy of GABA: A methodological review] | |||
Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, Volume 60, January 2012, Pages 29-41, Nicolaas A. J. Puts, Richard A. E. Edden | |||
[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811912011779# Current practice in the use of MEGA-PRESS spectroscopy for the detection of GABA] | |||
NeuroImage Volume 86, 1 February 2014, Pages 43–52, Paul G. Mullins, David J. McGonigle, Ruth L. O'Gormand, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Rishma Vidyasagar, C. John Evans, Cardiff Symposium on MRS of GABA, Richard A.E. Edden | |||
Methods Papers for the detection of GABA: | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC46781/?page=1 Localized 1H NMR measurements of gamma-aminobutyric acid in human brain in vivo] Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol.90, pp.5662-5666 June 1993 D L Rothman, O A Petroff, K L Behar, and R H Mattson | |||
[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/(SICI)1099-1492(199810)11:6%3C266::AID-NBM530%3E3.0.CO;2-J/abstract Simultaneous in vivo spectral editing and water suppression] NMR in Biomedicine Vol 11 Issue 6 pp.266-272 October 1998 M. Mescher, H. Merkle, J. Kirsch, M. Garwood and R. Gruetter | |||
[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/1522-2594(200103)45:3%3C517::AID-MRM1068%3E3.0.CO;2-6/full Brain GABA editing without macromolecule contamination] Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Volume 45 Issue 3 pp.517-520 March 2001 Pierre-Gilles Henry, Caroline Dautry, Philippe Hantraye and Gilles Bloch | |||
[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/nbm.1688/full Efficient γ-aminobutyric acid editing at 3T without macromolecule contamination: MEGA-SPECIAL] NMR in Biomedicine Volume 24 Issue 10 pp.1277-1285 December 2011 Jamie Near, Robin Simpson, Philip Cowen and Peter Jezzard | |||
[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mrm.24391/full Macromolecule-suppressed GABA-edited magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 3T] Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 68:657-661 (2012) Richard A. E. Edden, Nicolaas A. J. Puts and Peter B. Barker | |||
[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mrm.25549/abstract Spectral-editing measurements of GABA in the human brain with and without macromolecule suppression] Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Volume 74, Issue 6, pages 1523–1529, December 2015 Ashley D. Harris, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Peter B. Barker and Richard A.E. Edden | |||
Data Collection and Analysis of GABA MRS: | |||
[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jmri.23923/abstract Subtraction artifacts and frequency (Mis-)alignment in J-difference GABA editing] JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 38:970–975 (2013) C. John Evans, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Sian E. Robson, Frederic Boy,David J. McGonigle, Petroc Sumner, Krish D. Singh, and Richard A.E. Edden | |||
[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811914004248 Long-term reproducibility of GABA Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy] Neuroimage Volume 99 October 2014 Pages 191–196 Jamie Near, Yi-Ching Lynn Hoc, Kristian Sandberg, Chathura Kumaragamage, Jakob Udby Blicher | |||
[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mrm.25009/abstract Impact of frequency drift on gamma-aminobutyric acid-edited MR spectroscopy] Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 72:941–948 (2014) Ashley D. Harris, Benjamin Glaubitz, Jamie Near, C. John Evans, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Tobias Schmidt-Wilcke, Martin Tegenthoff, Peter B. Barker, Richard A.E. Edden | |||
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26172043 Tissue correction for GABA-edited MRS: Considerations of voxel composition, tissue segmentation, and tissue relaxations.] J Magn Reson Imaging 2015 Nov;42(5):1431-40 Ashley D. Harris, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, and Richard A.E. Edden | |||
[http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jmri.24478/full Gannet: A Batch-Processing Tool for the Quantitative Analysis of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid-Edited MR Spectroscopy Spectra] J Magn Reson Imaging (2014) 40,1445-1452, Richard Edden, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Ashley D. Harris, Peter Barker, and C. John Evans | |||
Applications Papers: | |||
Learning Studies: | |||
[http://cercor.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2015/12/01/cercor.bhv296 Local GABA Concentration Predicts Perceptual Improvements After Repetitive Sensory Stimulation in Humans] Cerebral Cortex, 2015, 1–7 Stefanie Heba1, Nicolaas A. J. Puts, Tobias Kalisch, Benjamin Glaubitz1, Lauren M. Haag, Melanie Lenz, Hubert R. Dinse, Richard A. E. Edden, Martin Tegenthoff and Tobias Schmidt-Wilcke | |||
Aging Related Studies: | |||
[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S105381191300339X Edited magnetic resonance spectroscopy detects an age-related decline in brain GABA levels] NeuroImage Volume 78, September 2013, Pages 75–82 Fei Gaoa, Richard A.E. Edden, Muwei Li, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Guangbin Wang, Cheng Liu, Bin Zhao, Huiquan Wang, Xue Bai, Chen Zhao, Xin Wang, Peter B. Barker | |||
Autism Studies: | |||
[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811913005685 GABA estimation in the brains of children on the autism spectrum: Measurement precision and regional cortical variation] NeuroImage Volume 86, 1 February 2014, Pages 1–9, W. Gaetz, L. Bloy, D.J. Wang, R.G. Port, L. Blaskey, S.E. Levy, T.P.L. Roberts | |||
[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S105381191300092X Decreased left perisylvian GABA concentration in children with autism and unaffected siblings] NeuroImage Volume 86, 1 February 2014, Pages 28–34 Donald C. Rojas, Debra Singel, Sarah Steinmetz, Susan Hepburn, Mark S. Brown | |||
Tourette Syndrome: | |||
[http://jn.physiology.org/content/114/2/808 Reduced GABAergic inhibition and abnormal sensory symptoms in children with Tourette syndrome] Journal of Neurophysiology Published 1 August 2015 Vol. 114 no. 2, 808-817 Nicolaas A. J. Puts, Ashley D. Harris, Deana Crocetti, Carrie Nettles, Harvey S. Singer, Mark Tommerdahl, Richard A. E. Edden, Stewart H. Mostofsky | |||
Motor-cortical plasticity: | |||
[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1053811913000402 Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy as a tool to study the role of GABA in motor-cortical plasticity] NeuroImage 86 (2014) 19–27, Charlotte J. Stagg | |||
Revision as of 01:13, 1 April 2021
Older methods and literature references will go here...
Extra section to be removed
Bottomley PA. Spatial localization in NMR spectroscopy in vivo. Ann NY Acad Sci 1987;508:333–48 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb32915.x
 |
 |
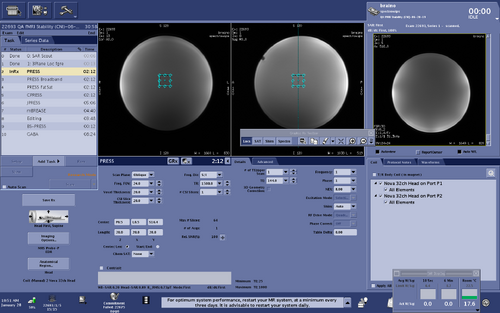
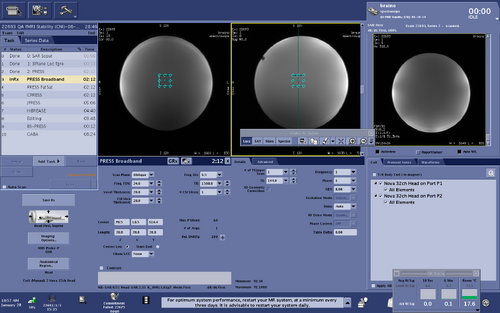
PRESS Broadband
The product refocusing pulses within PRESS can be replaced by broadband refocusing pulses described in M. Janich et al., Slice-selective broadband refocusing pulses for the robust generation of crushed spin-echoes, J Magn Reson, 223: 129 – 137 (2012) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2012.08.003 to reduce the CSDE.
 |
 |
CV 0 5000
CV0: spectral width The total spectral frequency width in Hz.
CV 1 4096
CV1: number of points The number of complex data points acquired per excitation.
CV 4 128 (1.5T) 64 (3T)
CV4: total number of scans The total number of excitations acquired per echo (cycle) when signal averaging. The value of CV4 must be an integer multiple of NEX.
CV 14 0
CV14: JPRESS Mode
0 (PRESS) standard PRESS acquisition, TE1 is set by sequence to minimum
1 (asym. PRESS) TE1 is set by user
2 (half-echo) standard JPRESS acquisition mode, echo acquired from echo top
3 (max-echo) maximum-echo mode described in [6]. For shortest echo time echo is acquired from echo top, for longer echo times data acquisition starts before the echo top.
CV 18 7
CV18: ROI edge sat/gradient mask There are three pairs of VSS RF pulses available at the edge of the Spectroscopy VOI. The VSS can be selected or deselected.
0 – no VSS RF pulses;
1 – S/I the superior and inferior pulses only;
2 – A/P the anterior and posterior pulses only;
3 – S/I and A/P, two pulse pairs;
4 – R/L the right and the left pulses only;
5 – R/L and S/I, two pulse pairs;
6 - R/L and A/P, two pulse pairs;
7 – R/L, A/P and S/I, three pulse pairs, this is the default value
This bitmask determines the polarity of the slice gradients of the three PRESS excitation/refocusing pulses and therefore the direction of the fat-water chemical shift. The corresponding bit set to 1 is negative polarity, 0 is positive.
0 – S/I, A/P and R/L all positive, this is the default value
8 – S/I negative, A/P and R/L positive
16 – A/P negative, S/I and R/L positive
24 – S/I and A/P negative, R/L positive
32 – R/L negative, S/I and A/P positive
40 – R/L and S/I negative, A/P positive
48 - R/L and A/P negative, S/I positive
56 – R/L, A/P and S/I all negative
CV 23 20
CV23: Refocusing Pulse Shape: PRESS refocusing pulse shape
20 – S-BREBOP-7500.rho, pw = 7.5ms
26 – flip_1803.rho, non-linear phase refocusing pulse used for CPRESS
-1 – default pulse set by PSD
CV 24 1
CV24: Feature flag
1 (no add) Store each single data acquisition in pfile.
2 (Bloch-Siegert) Bloch-Siegert TG calibration
PRESS FatSat
The dual BASING technique can be used for additional metabolite suppression, e.g. fat.
J. Star-Lack et al., Improved Water and Lipid Suppression for 3D PRESS CSI Using RF Band Selective Inversion with Gradient Dephasing (BASING), Magn Reson Med, 38, 311 – 321, (1997) https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.1910380222
CPRESS
CPRESS is a modified PRESS spectroscopic localization pulse sequence that replaces each of the two refocusing RF pulses with a pair of non-linear phase refocusing pulses. The non-linear phase refocusing pulses has been designed to operate at a lower maximum B1 requirement (0.15 G) while keeping the pulse width short (4.3 ms) and maintaining adequate bandwidth for spectroscopy application at 3T (1.2 kHz). At a TE of 42 ms, the short inter pulse delay (10.5 ms) between the refocusing pulses has a potential to provide improved sensitivity for J-coupled metabolites such as myoinositol (mI) and glutamate / glutamine (Glx) over conventional short TE (35 ms) PRESS sequence.
I. Hancu, Which pulse sequence is optimal for myo-inositol detection at 3T? NMR Biomed, 22: 426 – 435 (2009) https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1353
I. Hancu et al, Improved Myo-inositol Detection Through Carr–Purcell PRESS: A Tool for More Sensitive Mild Cognitive Impairment Diagnosis, Magn Reson Med, 65: 1515 – 1521 (2011) https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.22749
JPRESS
The two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy sequence consists of a series of spin-echo experiments with different echo times defined by the average echo time (TE) and the delta of echo times (User CV 16) employing PRESS localization. Adding the spectra gives a TEA-PRESS spectrum.
L. Ryner et al., Localized 2D J-resolved H-1 MR spectroscopy – strong coupling effects in vitro and in vivo, Magn Reson Imaging, 13: 853 – 869 (1995) https://doi.org/10.1016/0730-725x(95)00031-b
R. Schulte, Improved two-dimensional J-resolved spectroscopy, NMR Biomed, 19: 264 – 270 (2006) https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1027
mBREASE
mBREASE is a TEA-PRESS sequence with enabled STIR fat suppression, storage of each aquired FID to correct for frequency shifts and acquisition of reference data with different echo times to correct for water T2. It includes quantification of the choline signal using a voigt-lineshape model function in time domain and linear baseline in frequency domain. T2 corrected water signal is used as internal reference.
Editing
Spectral j-difference editing describes an advanced spectroscopy acquisition technique which is generally necessary to detect j-coupled markers and separate from co-resonant metabolite peaks. The implemented editing technique is based on the BASING technique described.
J. Star-Lack et al., Improved Water and Lipid Suppression for 3D PRESS CSI Using RF Band Selective Inversion with Gradient Dephasing (BASING), Magn Reson Med, 38, 311 – 321, (1997) https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.1910380222
J. Star-Lack et al., In Vivo Lactate Editing with Simultaneous Detection of Choline, Creatine, NAA, and Lipid Singlets at 1.5 T Using PRESS Excitation with Applications to the Study of Brain and Head and Neck Tumors, J Magn Reson, 133: 243 – 254 (1998) https://doi.org/10.1006/jmre.1998.1458
BS-PRESS
BS-PRESS is a voxel based TG calibration method described in [8]. The phase-based B1+ mapping technique using the Bloch-Siegert shift method encodes the B1 information into a signal phase resulting from off-resonant RF pulses within the sequence [9-11].
8. R. Noeske et al., Voxel Based Transmit Gain Calibration using Bloch-Siegert Shift Method for MR Spectroscopy, Proc 20th Annual Meeting ISMRM, Melbourne: 1733 (2012)
9. Sacolick et al., B1 Mapping by Bloch-Siegert Shift, Magn Reson Med, 63: 1315 - 1322 (2010)
10. Sacolick et al., Fast Radiofrequency Flip Angle Calibration by Bloch–Siegert Shift, Magn Reson Med, 66: 1333 - 1338 (2011)
11. Sacolick et al., Fast Spin Echo Bloch-Siegert B1 Mapping, Proc 19th Annual Meeting ISMRM, Montreal: 2927 (2011)
GABA
Older protocols (and sequences):
The CNI GABA spectroscopy MEGA PRESS protocol (CNI 32ch Participant GABA Spectroscopy) (located in CNI/Head), which can be run independently or added to an fMRI protocol.
There is now also the CNI-PRESS-SPECIAL (located in CNI/Head) protocol for GABA data collection, which can be run independently or added to an fMRI protocol. This is the latest protocol and the one to use.
Key Parameters for sequences:
This section (in the process of being updated) includes:
- parameters that require adjustment or checking prior to collecting spectroscopy data.
- additional setup sequences prior to running the spectroscopy sequence (example - shims) with setup details.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Automated voxel placement tools:
Typically MRS data is collected within a single voxel that needs to be manually prescribed. Manual prescription can lead to systematic bias and low data quality that may be caused by inexperienced users or inter-individual placement variability. To avoid these issues, and improve data collection quality, Matthew Sacchet has developed an automated voxel placement tool. It uses non-linear warping between native subject space and template space to identify precise voxel locations in scanner space. The tool is used in real-time during data acquisition and has been streamlined for efficient usage and low time cost.
Review papers of MRS of GABA:
In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy of GABA: A methodological review Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy, Volume 60, January 2012, Pages 29-41, Nicolaas A. J. Puts, Richard A. E. Edden
Current practice in the use of MEGA-PRESS spectroscopy for the detection of GABA NeuroImage Volume 86, 1 February 2014, Pages 43–52, Paul G. Mullins, David J. McGonigle, Ruth L. O'Gormand, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Rishma Vidyasagar, C. John Evans, Cardiff Symposium on MRS of GABA, Richard A.E. Edden
Methods Papers for the detection of GABA:
Localized 1H NMR measurements of gamma-aminobutyric acid in human brain in vivo Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol.90, pp.5662-5666 June 1993 D L Rothman, O A Petroff, K L Behar, and R H Mattson
Simultaneous in vivo spectral editing and water suppression NMR in Biomedicine Vol 11 Issue 6 pp.266-272 October 1998 M. Mescher, H. Merkle, J. Kirsch, M. Garwood and R. Gruetter
Brain GABA editing without macromolecule contamination Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Volume 45 Issue 3 pp.517-520 March 2001 Pierre-Gilles Henry, Caroline Dautry, Philippe Hantraye and Gilles Bloch
Efficient γ-aminobutyric acid editing at 3T without macromolecule contamination: MEGA-SPECIAL NMR in Biomedicine Volume 24 Issue 10 pp.1277-1285 December 2011 Jamie Near, Robin Simpson, Philip Cowen and Peter Jezzard
Macromolecule-suppressed GABA-edited magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 3T Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 68:657-661 (2012) Richard A. E. Edden, Nicolaas A. J. Puts and Peter B. Barker
Spectral-editing measurements of GABA in the human brain with and without macromolecule suppression Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Volume 74, Issue 6, pages 1523–1529, December 2015 Ashley D. Harris, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Peter B. Barker and Richard A.E. Edden
Data Collection and Analysis of GABA MRS:
Subtraction artifacts and frequency (Mis-)alignment in J-difference GABA editing JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 38:970–975 (2013) C. John Evans, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Sian E. Robson, Frederic Boy,David J. McGonigle, Petroc Sumner, Krish D. Singh, and Richard A.E. Edden
Long-term reproducibility of GABA Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Neuroimage Volume 99 October 2014 Pages 191–196 Jamie Near, Yi-Ching Lynn Hoc, Kristian Sandberg, Chathura Kumaragamage, Jakob Udby Blicher
Impact of frequency drift on gamma-aminobutyric acid-edited MR spectroscopy Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 72:941–948 (2014) Ashley D. Harris, Benjamin Glaubitz, Jamie Near, C. John Evans, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Tobias Schmidt-Wilcke, Martin Tegenthoff, Peter B. Barker, Richard A.E. Edden
Tissue correction for GABA-edited MRS: Considerations of voxel composition, tissue segmentation, and tissue relaxations. J Magn Reson Imaging 2015 Nov;42(5):1431-40 Ashley D. Harris, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, and Richard A.E. Edden
Gannet: A Batch-Processing Tool for the Quantitative Analysis of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid-Edited MR Spectroscopy Spectra J Magn Reson Imaging (2014) 40,1445-1452, Richard Edden, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Ashley D. Harris, Peter Barker, and C. John Evans
Applications Papers:
Learning Studies:
Local GABA Concentration Predicts Perceptual Improvements After Repetitive Sensory Stimulation in Humans Cerebral Cortex, 2015, 1–7 Stefanie Heba1, Nicolaas A. J. Puts, Tobias Kalisch, Benjamin Glaubitz1, Lauren M. Haag, Melanie Lenz, Hubert R. Dinse, Richard A. E. Edden, Martin Tegenthoff and Tobias Schmidt-Wilcke
Aging Related Studies:
Edited magnetic resonance spectroscopy detects an age-related decline in brain GABA levels NeuroImage Volume 78, September 2013, Pages 75–82 Fei Gaoa, Richard A.E. Edden, Muwei Li, Nicolaas A.J. Puts, Guangbin Wang, Cheng Liu, Bin Zhao, Huiquan Wang, Xue Bai, Chen Zhao, Xin Wang, Peter B. Barker
Autism Studies:
GABA estimation in the brains of children on the autism spectrum: Measurement precision and regional cortical variation NeuroImage Volume 86, 1 February 2014, Pages 1–9, W. Gaetz, L. Bloy, D.J. Wang, R.G. Port, L. Blaskey, S.E. Levy, T.P.L. Roberts
Decreased left perisylvian GABA concentration in children with autism and unaffected siblings NeuroImage Volume 86, 1 February 2014, Pages 28–34 Donald C. Rojas, Debra Singel, Sarah Steinmetz, Susan Hepburn, Mark S. Brown
Tourette Syndrome:
Reduced GABAergic inhibition and abnormal sensory symptoms in children with Tourette syndrome Journal of Neurophysiology Published 1 August 2015 Vol. 114 no. 2, 808-817 Nicolaas A. J. Puts, Ashley D. Harris, Deana Crocetti, Carrie Nettles, Harvey S. Singer, Mark Tommerdahl, Richard A. E. Edden, Stewart H. Mostofsky
Motor-cortical plasticity:
Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy as a tool to study the role of GABA in motor-cortical plasticity NeuroImage 86 (2014) 19–27, Charlotte J. Stagg